Please Check That the File Has the Correct Read Write Execute Permissions
File Permissions and Sharing Files
- Viewing File Permissions
- Irresolute File Permissions
- Collaboration and File Permissions
Viewing File Permissions
File permissions provide a way of controlling whether other people can read (or even modify) your files. This page discusses how file permissions work in Unix and how to change them.
Y'all can view the permissions on a file by typing "ls -l filename". For example, here is the consequence of typing "ls -l test.html" in my home directory:
-rw-r--r-- one eva statsusers 3325 Aug 2 09:15 test.html
Note: "eva" and "statsusers" are the user and group which own the file. They tin can be ignored when you are working on your ain files. If you are collaborating and want files which more than than 1 person tin edit, you need to pay attending to group ownerships.
The "-rw-r--r--" is the part of the output that shows the permissions. To understand what it means, we need to break it into four parts.
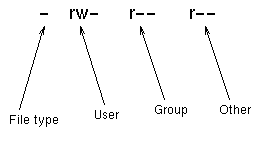
The commencement graphic symbol indicates the file type. Hither it is a nuance because test.html is an ordinary file. It could also exist a d for a directory, or various other letters for more obscure types of file.
The adjacent nine characters autumn into three sets of three, corresponding to the access rights of the user who owns the file, the grouping which owns the file, and all other users. The three characters in each set indicate whether users in the relevant category may read, write or execute the file. An r, westward or x means that the users do have the respective correct, while a nuance means that they do not.
Thus in the above case, eva (the user who owns the file) has the access rights rw-, meaning that she may read and write the file simply not execute information technology (since it'south an HTML file, executing it wouldn't brand much sense). Everyone else has the admission rights r--, meaning that they may read the file but not write or execute it.
The following tabular array shows what read, write and execute permissions hateful for ordinary files and for directories.
| File | Directory | |
|---|---|---|
| Read | Can read the file | Can list files in the directory |
| Write | Tin can edit the file | Can create and delete files in the directory |
| Execute | Can run the file as a programme | Can change to the directory |
A notation for those who are concerned about the privacy of their files just want to put up web pages. To view a file, i must be able to change to its directory. Thus if your web pages are to be visible, your dwelling directory and your public_html directory must both exist executable by everyone. This is the default for your home directory but you may need to blazon chmod 711 public_html to make your public_html directory accessible.
More nearly setting up your own web pages
Irresolute File Permissions
File permissions are changed by using the chmod command. The format of this command is
chmod permissions list_of_files
"permissions" is a iii-digit octal number where the three digits stand for to the access rights of the user who owns the file, the group and other users, equally discussed to a higher place. Each octal digit is the sum of 4 if read permission is granted, two if write permission is granted and 1 if execute permission is granted. Here are the most commonly needed permissions:
- 755 ways you lot can do anything with the file or directory, and other users tin read and execute information technology but not alter it. Suitable for programs and directories yous want to make publicly available.
- 644 means you can read and write the file or directory and other users can only read it. Suitable for public text files.
- 711 means yous can do anything with the file or directory and other users can merely execute it. Suitable for directories where you don't desire other people browsing through the contents but practise want to give them access to selected files. This is the default for your dwelling directory and the minimum access required for your public_html directory if you have a personal website.
- 700 means you can do annihilation with the file or directory and other users have no access to it at all. Suitable for private directories and programs.
- 600 ways you can read and write the file or directory and other users take no access to information technology. Suitable for individual text files.
To make a directory and everything in information technology readable past all other Maths users, type
chmod -R go+rX my_directory
- -R ways recursive (go downwards into subdirectories)
- go means change permissions for Group and Other
- +rX means add Read permissions, and add execute permissions where appropriate (to be precise, for all directories and for files which already have execute permission for some users).
You can change the default permissions on new files you lot create using the umask control. The format of this command is
umask octal_number
where octal_number is a 3-digit octal number representing what each category of user may not do with the file.
- umask 022 ways that other users may not edit your files merely may read them and execute them where appropriate.
- umask 066 means that other users may not modify or read your files but may execute them where appropriate (for example, they can change to subdirectories of your home directory).
- umask 077 means that other users may not access your files at all. (This is the default.)
Type man chmod or human being umask for more information.
Collaboration and File Permissions
In the higher up discussion, the permissions for the group and other users were always the aforementioned, because nearly of the default Unix groups nosotros have in the Maths departments are besides large for it to make sense to give the group more rights than everyone else. For case, the "statsusers" grouping contains everyone in the Statslab.
Sometimes, though, a small group of users are collaborating on a projection and find it useful to take files which they can all edit. If this applies to y'all, please email help@maths to request that a Unix grouping be created for your collaboration.
One time your group has been ready, you tin create a grouping-writable directory for them (replace "ourgroup" with the actual name of your group and "ourdirectory" with anything y'all like).
mkdir ourdirectory chgrp ourgroup ourdirectory chmod 2775 ourdirectory
What do these commands hateful?
-
mkdir ourdirectoryjust creates the directory. -
chgrp ourgroup ourdirectorymeans that the directory will belong to your new group. -
chmod 2775 ourdirectorydoes two helpful things to the directory'south file permissions. Kickoff, it means that people in your grouping tin can create new files in that directory, but other people cannot. Second, the 2 on the kickoff sets the "setgid fleck", which in this context ways that new files in the directory will automatically be owned by "ourgroup".
If you have trouble editing files in your communal directory:
- Apply ls -l to check group ownerships and file permissions.
- Employ chgrp ourgroup name to make the file or directory "proper name" vest to your grouping.
- Employ chmod 2775 dirname if you are having trouble creating files in directory "dirname".
- Use chmod 664 filename if yous can't edit a specific file.
Source: https://www.maths.cam.ac.uk/computing/linux/unixinfo/perms
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Please Check That the File Has the Correct Read Write Execute Permissions"
Posting Komentar